
We collect basic website visitor information on this website and store it in cookies. We also utilize Google Analytics to track page view information to assist us in improving our website.
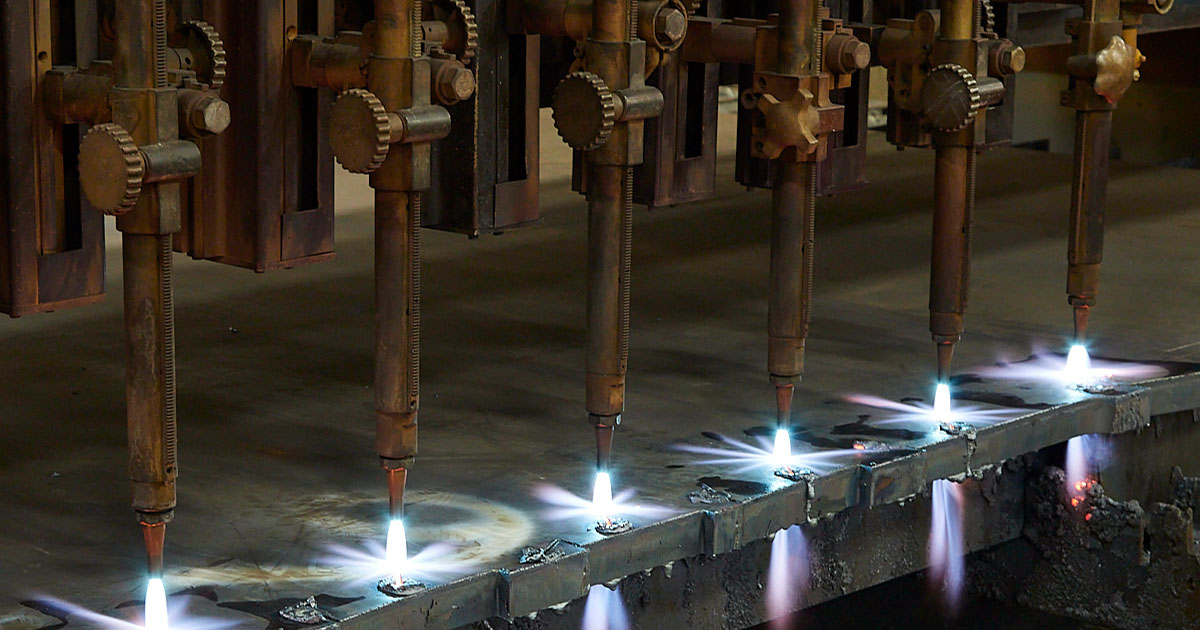
Flame cutting is the go-to method for slicing through thick steel, making it a valuable tool for all kinds of industrial settings.
It's where precision meets efficiency, especially when it comes to heavy-duty applications. At Amber Steel, we pride ourselves on our years of expertise with cutting-edge flame cutting techniques to tackle even the most formidable projects with skill and precision.
In this post, we’ll zero in on the challenges of and best practices for flame cutting thick steel. Whether it's the colossal ships, structural steel for construction, or robust oil and gas machinery, mastering these challenges is key to achieving high-quality flame cutting results.
Let's cut to the chase and explore how every flame cutting challenge is an opportunity to innovate.
At Amber Steel, we specialize in laser, plasma and flame cutting, and have always been a "total source" service for the production of quality steel products. Quality is achieved by utilizing the right production technique for the right product. Our continual investment in equipment and technology enables us to offer clients many production alternatives to achieve exact product specifications and tolerances. If you’re interested in learning more about steel cutting or have a project in mind that you would need our expertise on, do not hesitate to reach out. We’re always one email or phone call away.
Why do the heavy hitters of industry — think shipbuilders, mining machinery manufacturers, and bridge engineers — often turn to flame cutting?
The answer lies in its unique blend of technical advantages tailor-made for handling the heavyweight contenders of the steel world.
Precision: When it comes to thick steel, flame cutting allows for precise cuts in steel plates that can be several inches thick, a feat not all cutting methods can claim with the same level of finesse.
Cost-Effectiveness: Flame cutting scores high on cost-efficiency, especially for thick materials where alternative methods might cost a fortune in comparison.
Versatility: Whether it's a straight line or a complex contour, it handles diverse shapes with ease. This adaptability makes it a go-to solution for everything from the backbone of skyscrapers to the hulls of ships.
Simplicity: While "simple" might not be the first word that comes to mind when you think about cutting through several-inch-thick steel plates, flame cutting offers a straightforwardness that's hard to beat. It’s reliable, uncomplicated and accessible.
Imagine trying to perfectly toast a marshmallow over a campfire, aiming for that golden brown without turning it into a charred lump.

That's a bit like the careful balance required in flame cutting, where the goal is to melt and cut steel with surgical precision without turning the surrounding areas into a metallurgical mess.
The challenge here is not just to cut, but to cut without compromising the integrity of the steel beyond the cut line. Flame cutting heats steel to its melting point, around 1,370°C to 1,540°C (2,500°F to 2,800°F). This intense heat needs to be controlled with extreme precision.
Thermal distortion is what happens when the heat from cutting decides to go on a little tour into the surrounding metal, causing it to warp or distort. In thick steel, this is even more pronounced due to the sheer volume of metal and heat involved.
Another concern is the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ), which is the area around the cut where the steel hasn't melted but has still felt the heat. This area can undergo changes in microstructure, affecting the steel's mechanical properties.
Heat management in flame cutting for thick steel is an artful balance of science, technology, and human skill.
Preheating: By warming the steel before cutting it, we reduce the risk of thermal shock and distortion, making the cutting process smoother and the results more predictable.
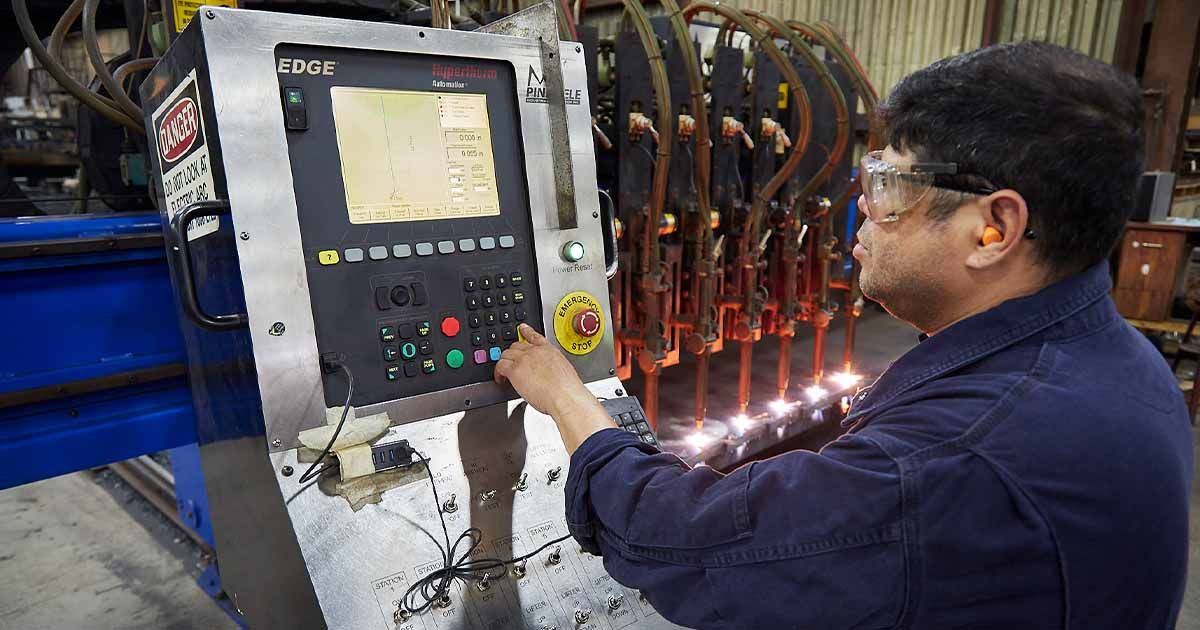
Utilizing Technology: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems offer precise control over the process, while the expertise of seasoned operators ensures adjustments are made in real-time.
Controlled Cutting Speed: The cutting speed must be carefully managed to balance efficiency with precision, avoiding excessive heat buildup.
Post-Cut Cooling Practices: After the cut, controlling how the steel cools down is crucial. Techniques like covering the cut parts with insulating blankets or using controlled environment cooling help minimize stresses and distortion.
Controlling the heat ensures that the final product is cut to size while retaining its structural integrity and strength, ready for whatever comes next.
The thickness of the steel dictates everything from the heat required to the speed of the cut, which impacts both efficiency and quality.
Thicker steel requires more heat to be cut through, which can slow down the process and increase the heat-affected zone (HAZ). Thicker materials also present challenges like increased dross (residual material left from the cutting process), rougher cut surfaces, and wider kerf width (the width of the material removed during cutting).
On the flip side, thinner materials heat up and cool down quicker, allowing for faster cuts but also raising the risk of warping due to rapid temperature changes.
It takes a comprehensive approach that combines technology, experience, and careful planning to overcome the challenges posed by material thickness in flame cutting.
Preheating: Just as with managing heat, preheating the steel can help minimize thermal gradients and reduce the risk of thermal stress and distortion, particularly in thicker materials. This makes the cutting process more uniform and predictable.
Optimized Cutting Parameters: Adjusting cutting parameters such as flame intensity, cutting speed, and oxygen pressure for different material thicknesses is essential. Experience, along with guidelines from equipment manufacturers, is key in finding the optimal settings for each job.
Multiple Pass Cutting: For exceptionally thick materials, using multiple passes can be an effective way to manage heat input and improve cut quality. The first pass preheats and begins the cut, with subsequent passes deepening the cut until completion.
Utilizing Technology: Advanced CNC systems provide precise control over the cutting process, allowing for adjustments in real-time to accommodate materials of varying thicknesses. This technological edge ensures consistent quality and efficiency across different projects.
Managing these variables meticulously ensures that each piece of steel meets the correct dimensions and high standards expected of industrial products.
Selecting the right gas mixture plays a significant role in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of the cutting process, especially when dealing with thick steel.
First, the gas mixture directly impacts the flame's temperature, which in turn affects how efficiently and cleanly the steel can be cut. Higher flame temperatures allow for quicker cuts but require careful management to avoid compromising cut quality.
Additionally, certain gases enhance the steel's oxidation process during cutting. This allows for a faster, cleaner cut by helping to expel the molten metal more effectively.
Finally, every gas comes with its own set of safety and cost implications. Factors like flammability, health hazards, and price per cubic foot must be balanced against the gas's cutting performance to make an informed choice.
Oxygen: Pure oxygen is used to increase the flame temperature and facilitate the cutting process.
Acetylene: Known for its high flame temperature and efficiency in cutting thick steel, acetylene is often chosen for jobs requiring precision and speed. However, it's more expensive than other gases and has a narrower range of safe operating conditions.
Propane and Propylene: These gases offer a balance between performance and cost. They have lower flame temperatures than acetylene but are safer to handle and more economical, making them suitable for cutting thicker steel sections where the highest cutting speed is not the primary concern.
Natural Gas: Natural gas is an economical option for flame cutting operations, although its performance is lower than acetylene or propylene. Its availability and cost can make it an attractive choice for large-scale or less precision-critical cutting tasks.
Choosing the right gas mixture for each project ensures both the efficiency and quality of the cutting process, as well as the overall success of the fabrication process that follows.
Application-Specific Selection: The best approach to gas selection involves considering the specific requirements of the job, such as material thickness, desired cut quality, and budget constraints.
Combining Gases: Sometimes, a combination of gases can be used to optimize performance, taking advantage of the beneficial properties of each gas.
Trial and Error: Experimenting with different gas mixtures can help identify the best option for balancing cut quality, speed, and cost for specific applications.
Flame cutting, with its unique challenges and technical demands, is not just about having the right tools — it's about having the right partner.
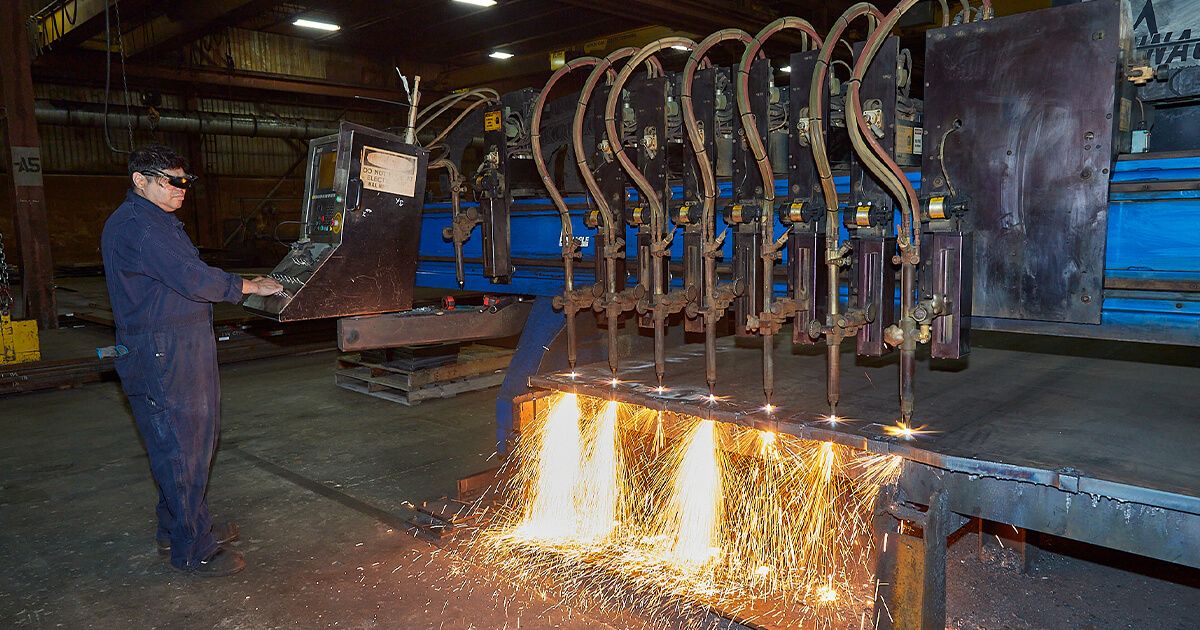

At Amber Steel, our commitment to quality, precision, and customer satisfaction is at the core of everything we do. We understand that the success of your projects depends on the accuracy and quality of the cutting process. That's why we've honed our skills, invested in the latest technology, and cultivated a team of experts who are passionate about delivering excellence.
Choosing Amber Steel as your flame cutting partner means entrusting your projects to a team that views your success as their own. We take pride in our ability to meet the specific needs of each client, whether it's adjusting based on material thickness, mastering heat management, or choosing the correct gas mixture.
Your projects demand precision, quality, and a commitment to excellence. At Amber Steel, we're ready to deliver on those demands, ensuring that every cut is a step toward the successful completion of your project. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your flame cutting needs and help bring your vision to reality.